The degree of protection of bulletproof products has several different classification criteria, and the NIJ bulletproof standard developed by the National Institute of Justice is currently a relatively common standard in the world. Many bulletproof product manufacturers and criminal justice agencies use this standard. The specified test method is used to determine the protection criteria for bulletproof products.
The bulletproof vest is commonly used in the US NIJ standard. There are 6 levels in this standard: I, IIA, II, IIIA, III, IV.
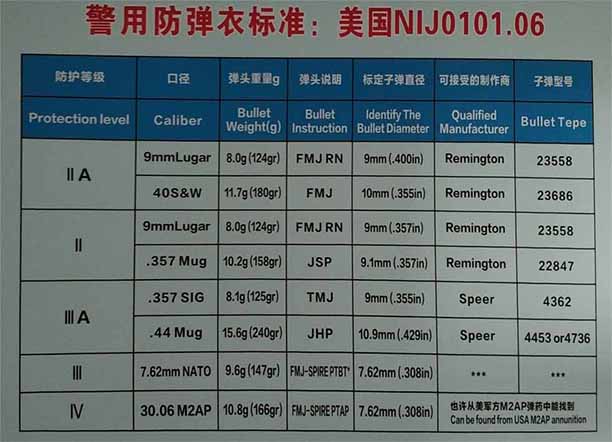
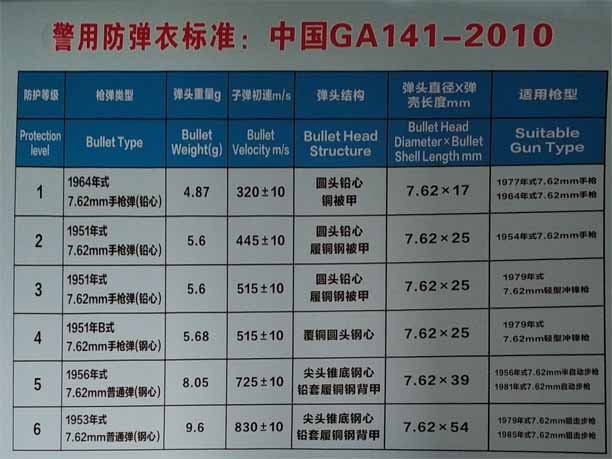
The protection ability is from low to high. Among them, the IIIA class requires 9mm pistol bullets that can prevent micro-shooting, and the bullet speed is 420m/s. The level below IIIA is anti-9mm pistol, and the bullet speed is below 360m/s.
Most customers generally require the protection level of bulletproof vests to be Class IIIA. Class III protection is to add two 300mm*250mm ceramic composite boards before and after the body armor. The thickness of each board is 18mm and the weight is 2.6kg. This level requires Anti-M80 bombs (7.62*51 bombs, bullet speed: 800m/s) There are also ordinary bombs fired by AK-47 and 56-type rifles.
Class IV also requires the addition of a ceramic plate with a thickness of 21 mm and a weight of 3.3 kg. An armor-piercing projectile capable of preventing M1 emission is required, and the bounce speed is 850 m/s.
The bulletproof armor is below the soft grade IIIA. The bulletproof layer material that does not require the soft bulletproof coating of the ceramic board has domestic and imported materials. The domestic material is white super high strength polyethylene fiber; the imported material is KEVLAR. Yellow; the price of bulletproof clothing is related to the material used, and it is also related to the protective area. The larger the area, the higher the price. The common body armor has three kinds of protection areas: vest type (0.27 square meters), vest type (0.32), full protection type. (with ankle guard 0.60).
 English
English German
German French
French Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Portuguese
Portuguese Ukrainian
Ukrainian Arabic
Arabic Italian
Italian Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian Greek
Greek Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Macedonian
Macedonian Malay
Malay Maltese
Maltese Norwegian
Norwegian Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Romanian
Romanian Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Urdu
Urdu Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Yiddish
Yiddish