First, the military and informal equipment of Russia, Belarus, Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic:
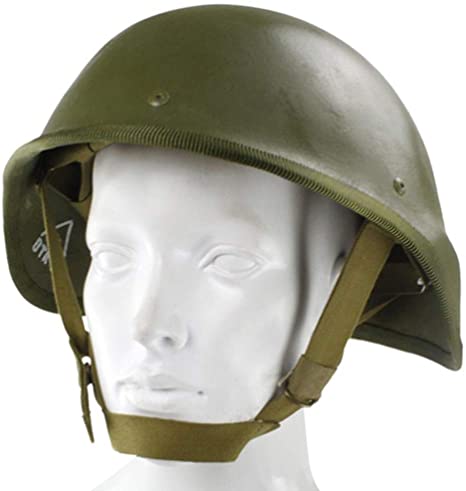
1.SSh-68
The positioning of the SSh-68 is not a bulletproof helmet, so there is no guarantee that it can block the impact of bullets, In Russia, the SSh-68 has been largely replaced by newer helmets such as the 6B7-1M and 6B47.
.png)
2.6B26
3.6B27
6B26 and 6B27 are shown in the 2006 year, belonging to Part of the Ratnik infantry system.
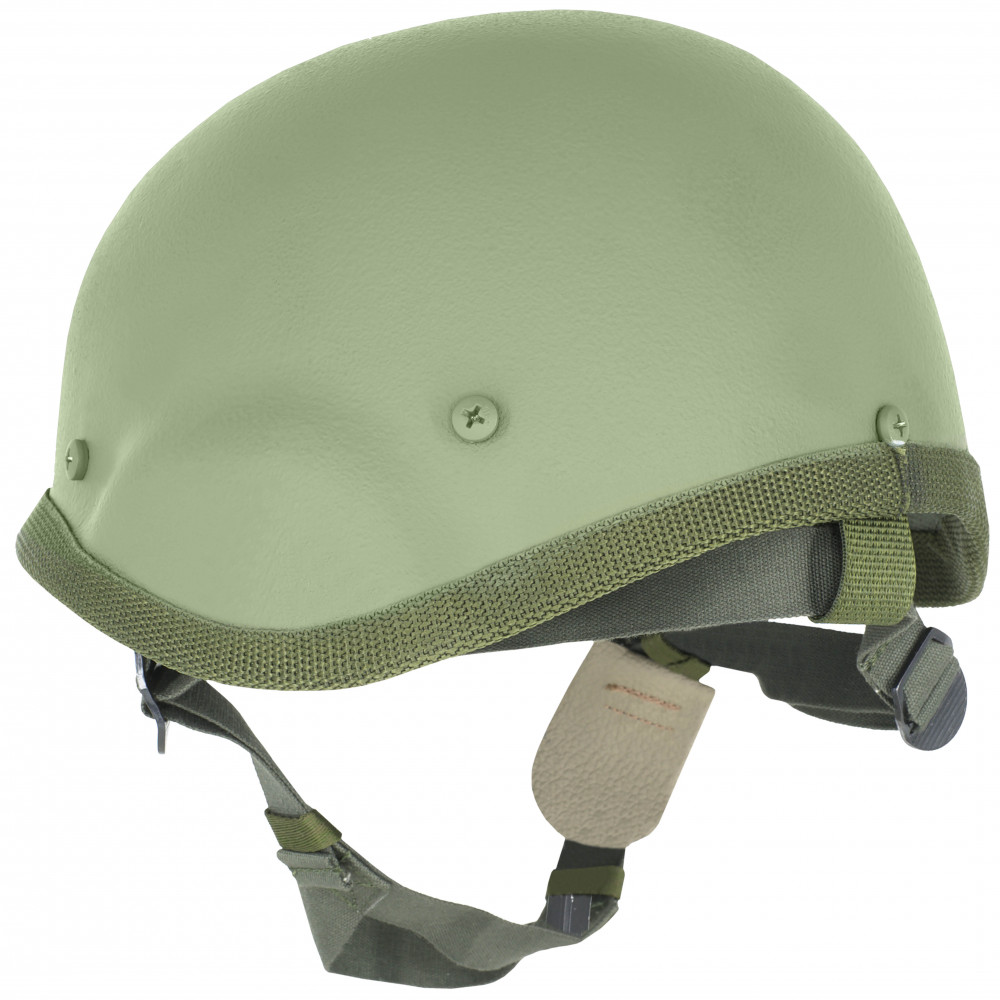


4.6B47
The metamorphosis from 6B26 and 6B27 helmets released in 2006 belong to the same Ratnik infantry system.
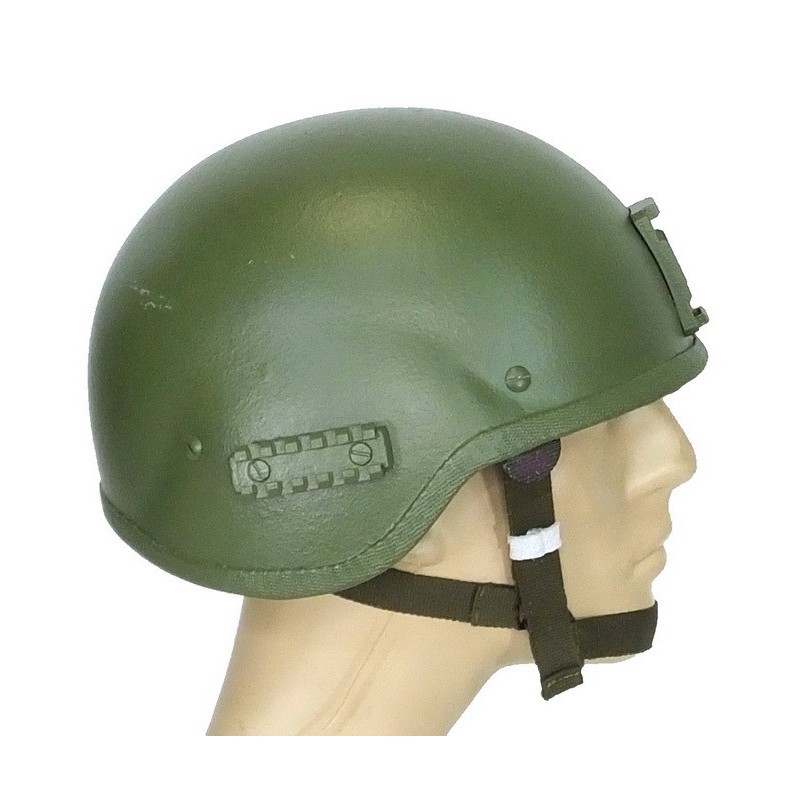

5.ZSh-1-2M
At the beginning of 2000, the development of such equipment was carried out and ZSH-1-2M became one of these helmets. The advantage is that it comes with a protective mask, which can effectively resist frontal injuries. The disadvantage is that the weight of the helmet is too heavy and cannot be worn for a long time.
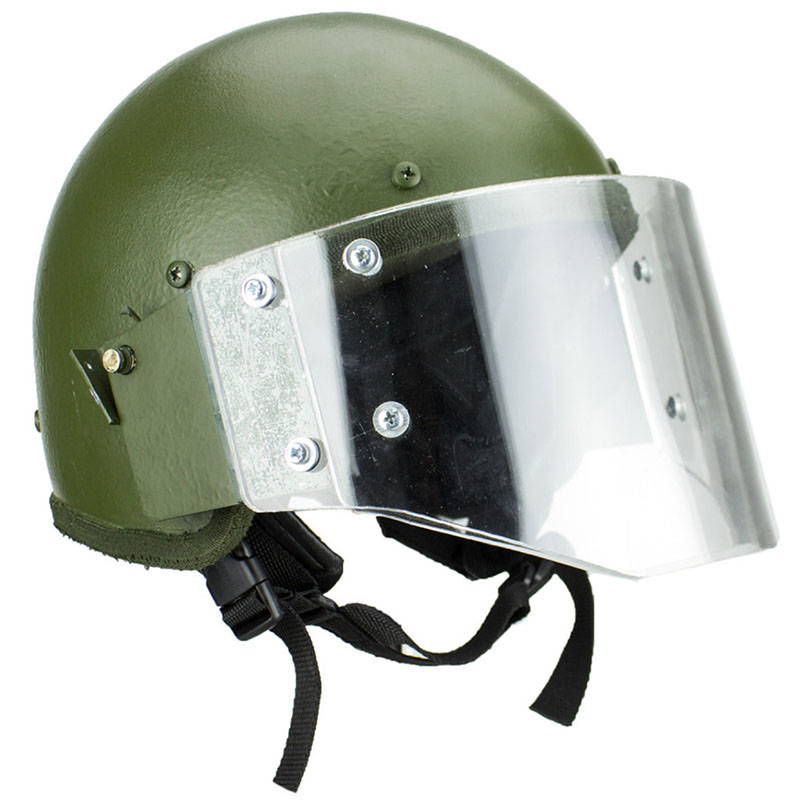

6.LShZ 1+
The LShZ 1+ helmet is a serious update of ArmoCom’s previous creation, known as LShZ-2DT. This helmet has been used for more than 10 years all over Russia by their special units of the Federal Security Service (FSB). It’s now being replaced with the Lshz 1+ among the FSB units that were in need of a redesigned helmet. It was created in 2012 especially for the Russian special forces.As the name “LSHZ 1+” clearly indicates, this helmet has the protection class 1+ according to Russian standards, which is in principle equivalent to the protection standard IIIA for NIJ (Western classification of armor protection).
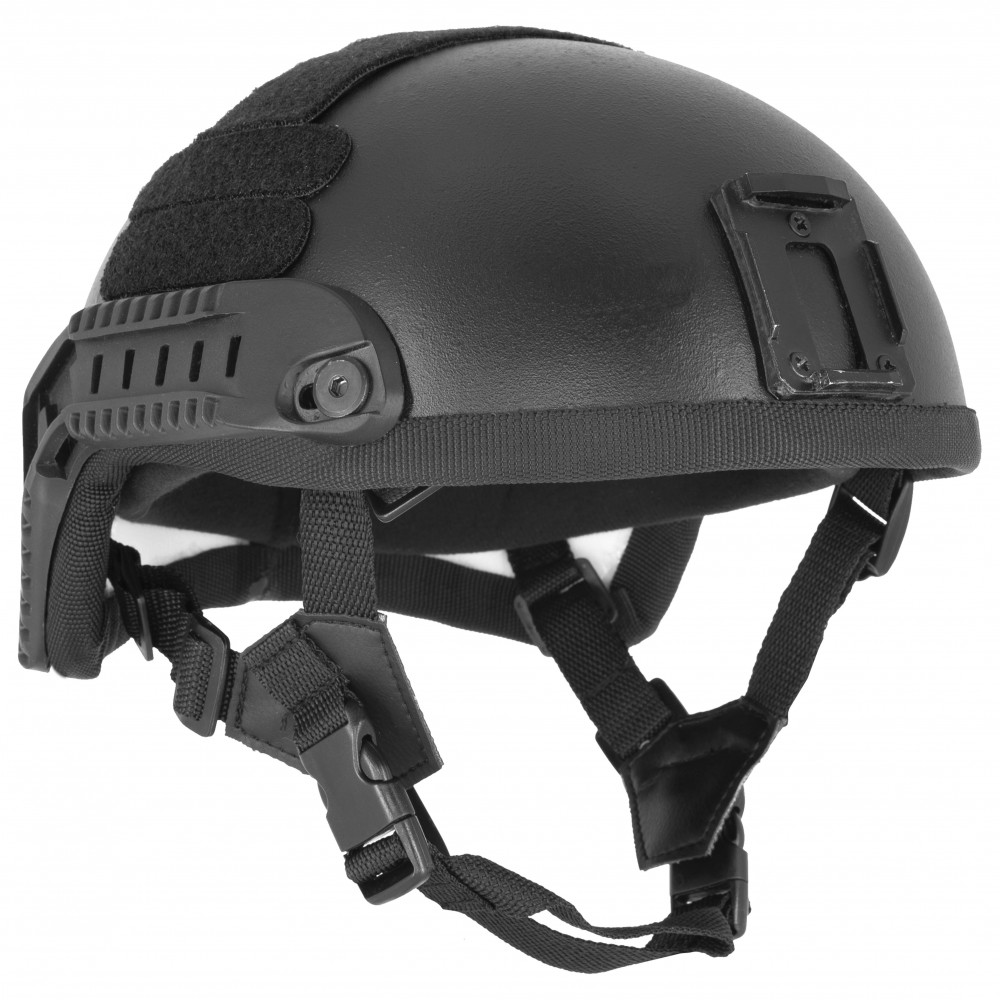

7.5.45 Design Spartan I
Helmet design ensures impact resistance under direct sunlight, rain and snow, as well as after the short exposure to the open fire. Wide adjustment range includes different head sizes and non-standard shapes (elongated/flat). Helmet does not restrain the freedom of motion.
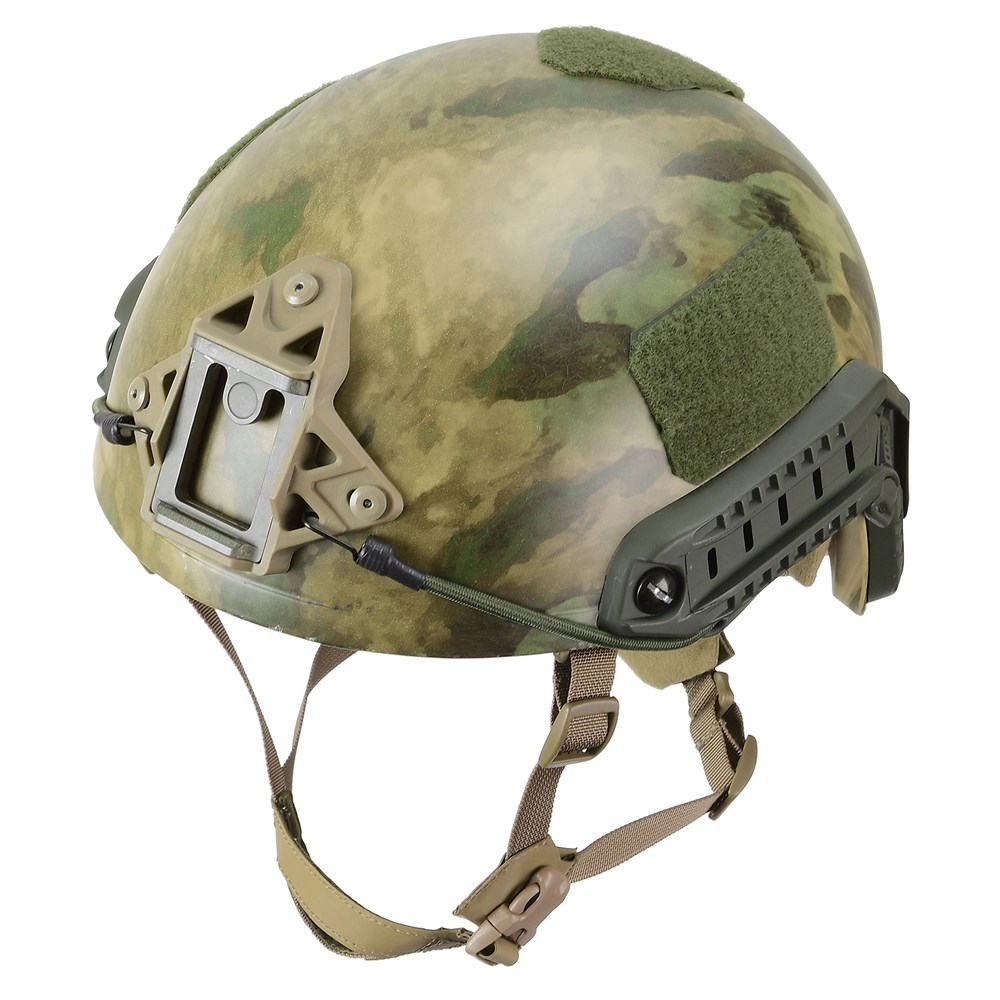

8.Ops-Core FAST Ballistic
Compared to standard combat helmets, the FAST helmet offers up to 25% weight reduction and is notable for its early use of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fibers (UHMWPE) in its design. It was also designed to allow outside features such as wearing communications headsets that can be attached with rail adapters.
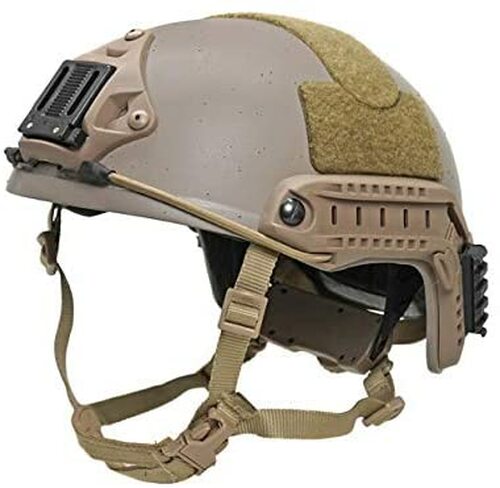

Followed by Ukrainian Army and Volunteer Force Equipment
1. SSh-40
2. SSh-60
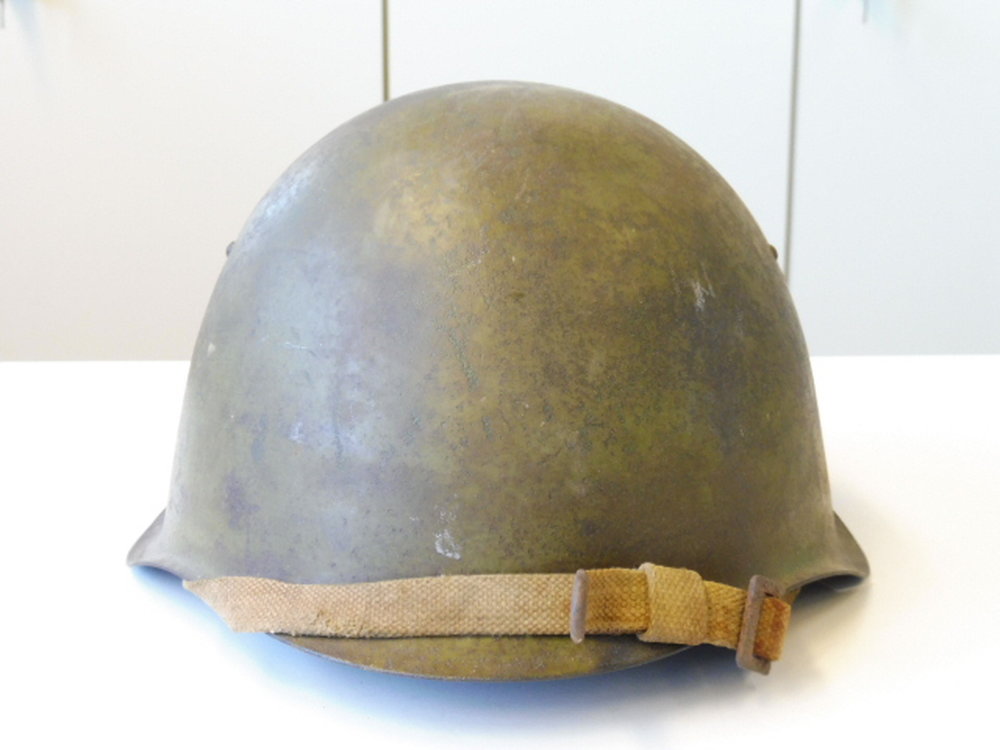
3. SSh-68
The SSh-40 was the most common Soviet helmet in service during World War II. The rivet location of the SSh-40 is due to the newly introduced lining, which is simpler and stronger than the previous version. The SSh-40 was only made in three sizes 1-3. The SSh-40 was complemented by the SSh-60, which entered service in the 1960s and was eventually replaced by the SSh-68, although many remained in use during Soviet times and beyond.

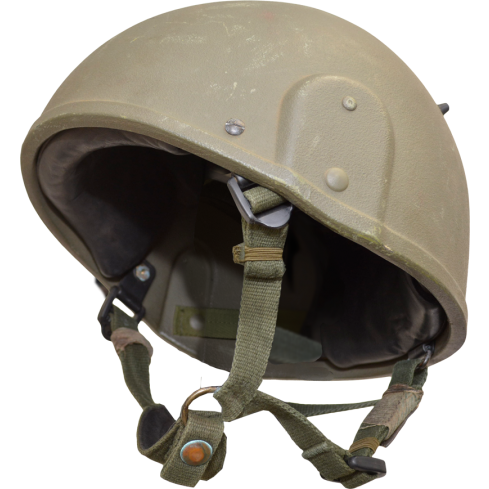
4. Mk 6
The Mk 6 helmet is a standard combat helmet of the British army. Compared with the old military helmet, the Mk 3 helmet, which it replaced since 1986, it is easier to carry personal radios and gas masks, and has better ear protection. good. This helmet is produced by NP Aerospace. The original color of the Mk 6 helmet is dark green. The British army also adds a helmet cover to the outer helmet for military camouflage. The colors include green DPM camouflage, jungle, Desert pattern, pure white helmet cover for polar combat and blue helmet cover for UN missions. Sometimes nicknamed the Battle Bowler, the term was used to describe the Brody helmet worn by the British during World War II.

5. Mk 7
The Mk 7 helmet is the latest active combat helmet in the British Army, officially known as the GS Mark 7 combat helmet, replacing the older Mk 6A helmet (2005 year) and the Mk 6 helmet.
The Mk7 helmet, introduced in June 2009 as an urgent operational requirement equipment, is similar in bulletproof effect to the Mk6A helmet, but has an improved appearance. The raised leading edge allows soldiers to shoot from a prone position without the trailing edge of the helmet hitting the body, which depresses the leading edge and obstructs the viewing angle. Moreover, the stability of the attached night vision device has also been improved.
In addition, the weight of the Mk7 helmet is 1kg less than the old size 6 helmet which weighed 1.5kg, and the helmet straps hold the effect better. The original base color of the inner helmet is light brown, which is also different from the black of the Mk 6A helmet and the dark green of the Mk6 helmet. It was first put into actual combat use in the Afghan war.
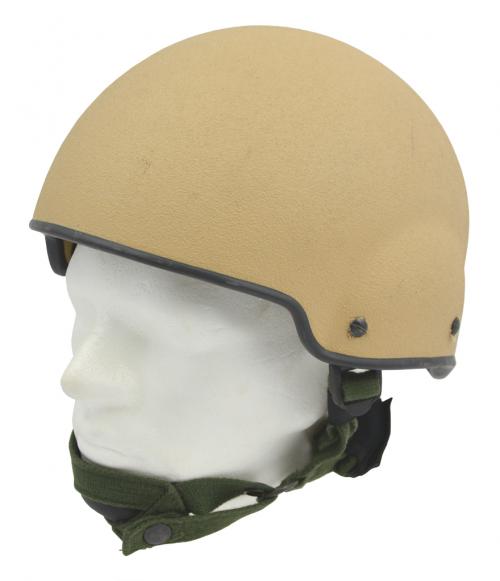

6. M92
The Gefechtshelm M92 (or Gefechtshelm Schuberth B826) is the Bundeswehr's standard combat helmet, first introduced in 1992 to replace the earlier M1956 steel helmets used during the Cold War. It is made of aramid composite and is used by all branches of the Bundeswehr.
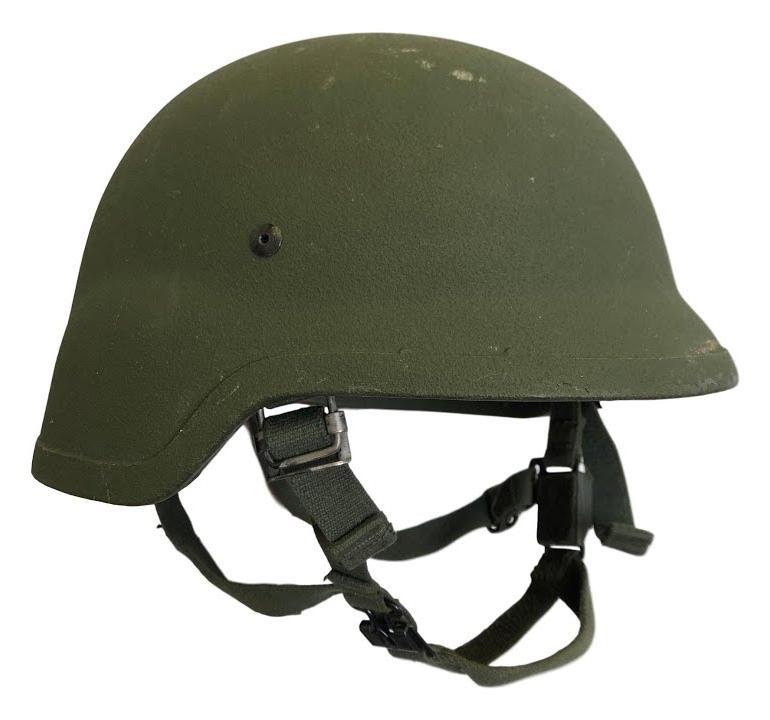

7. PASGT
PASGT, the full name of Personnel Armor System for Ground Troops, is a piece of individual equipment assembled by the U.S. military since 1983, consisting of a helmet and a bulletproof vest. Among them, the helmet is made of 19 layers of 1500 denier Kevlar 29 aramid fiber fabric. Because its shape is similar to the M35 steel helmet of the Nazi German army during World War II, the PASGT helmet has now been replaced by advanced combat helmets and interceptor bulletproof vests. Many countries are still using this helmet, and it is regarded as the three benchmarks of bulletproof helmets together with FAST and MICH.
.jpg)
8. ACH
Advanced Combat Helmet or Advanced Combat Helmet, abbreviation ACH helmet, is the active combat helmet of the U.S. Army, developed by the United States Army Soldier Systems Center as a new generation of protective helmets for the U.S. Army, and its design is a derivative of the MICH helmet (Modular Integrated Communications Helmet).

9. Ops-Core FAST Ballistic
10. Uarms Tor-D
HighCut combat helmet by Ukrainian company UaRms.
The helmets were designed and manufactured by a small group of developers in collaboration with soldiers and emergency services from across Europe to provide security for previously poorly equipped Ukrainian soldiers, allowing them to be better used up and protecting the user's Safety.
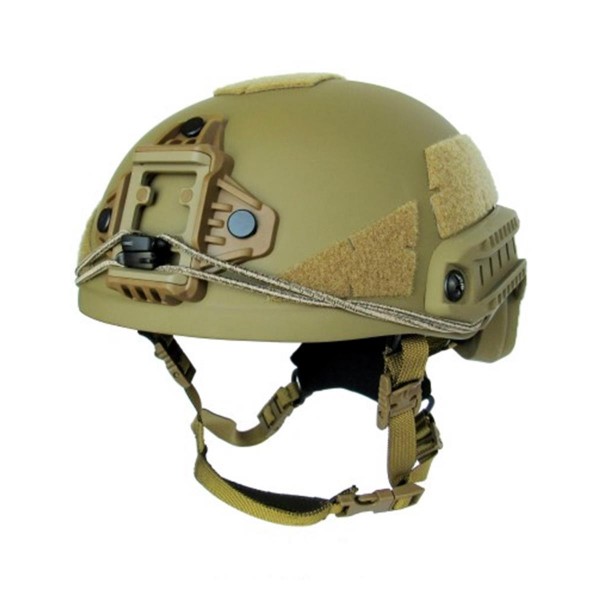

11. Team Wendy Exfil
Team Wendy EXFIL Ballistic utilizes a hybrid composite shell for an optimal fit, and a bolt-free CAM FIT fixation adapts to the head shape for comfort and stability. Zorbium foam padding protects against impacts and allows for overhead communication headbands. A customizable fit is achieved through a set of removable comfort pads. The lanyard compatible Wilcox shroud secures any standard NVG mount.
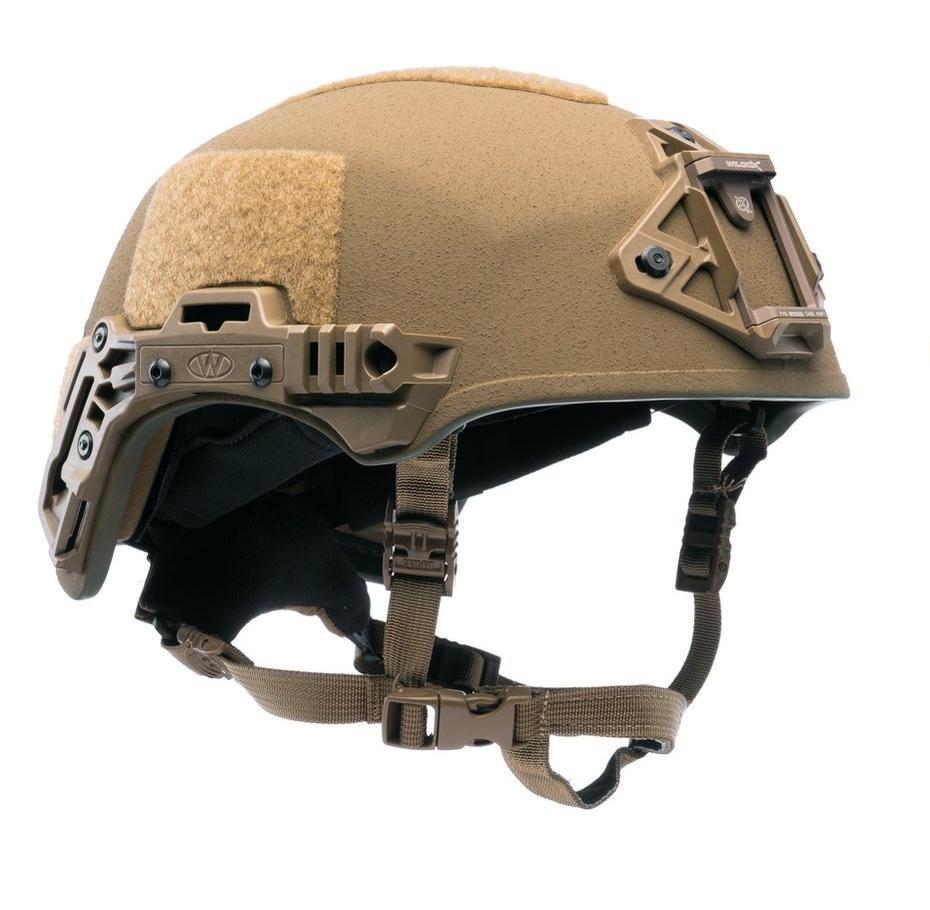

12. wz. 2005
wz.2005 is the prescribed helmet of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland, carried out at the Technical Institute of Military Equipment and the company Maskpol SA. A new helmet was developed together. The shape of the shell is modeled on structures such as the American PASGT helmet and the German Schubert helmet.
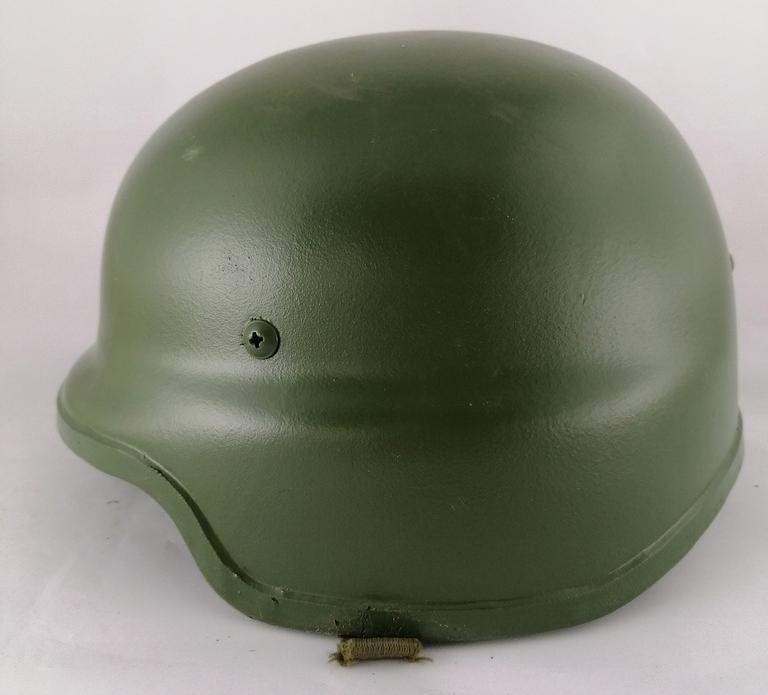

13. Hjälm 90
This helmet was used by the Swedish Armed Forces as a replacement for the old steel helmet, the helmet m/1937. The helmet interior was originally a plastic construction to which a leather pad filled with cotton and foam was applied, but was upgraded to a mesh interior that made the helmet more comfortable and less prone to wobbling.

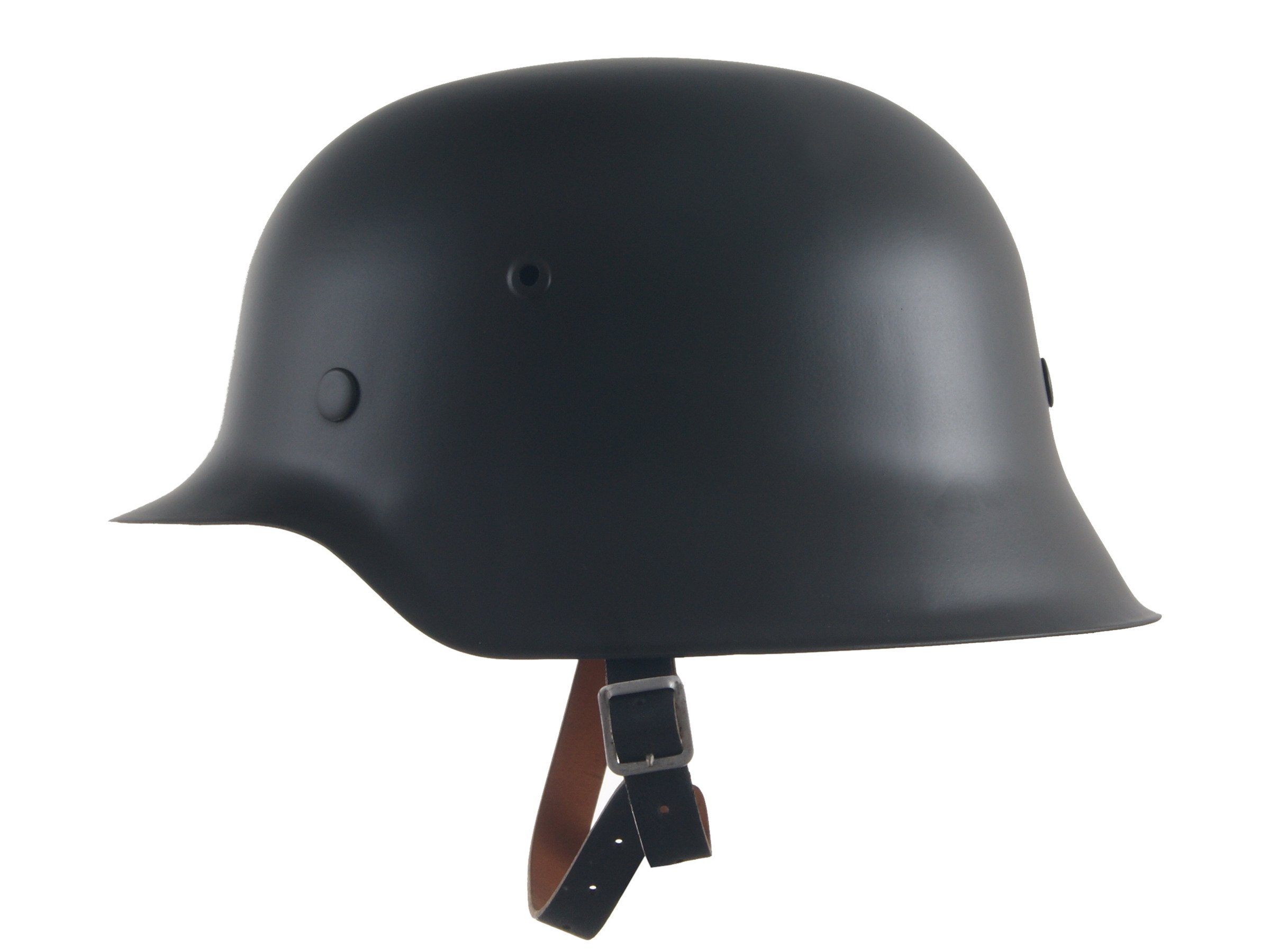
14.88 steel helmet
The 88-type steel helmet (Japanese: 88-type iron hat) is a helmet used by the Japanese Self-Defense Forces, and also used by the Coast Guard and the police.
The Type 88 steel helmet is the successor to the Type 66 steel helmet. It was developed by the Technical Research Department in 1978 and installed in 1988. Made of bulletproof composite fiber, it can protect the fragmentation of shells below 155mm, and it is lighter than the 66 type, and improves the problem that the helmet will be blocked by the steel helmet when using the Fenghe 64 7.62mm automatic rifle. The problem, the Self-Defense Force is very satisfied with it , so a large amount of equipment is available in a short period of time.
After the 1990s, the individual night vision device JGVS-V8 has been widely equipped, and it is also compatible with the Type 88 steel helmet and can be mounted. After that, the Air Self-Defense Force, the Maritime Self-Defense Force, and the Base Guard also gradually adopted the Type 88.

The helmet is introduced here first, and the next issue will introduce the tactical vests used in the Russian-Ukrainian war.
 English
English German
German French
French Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Portuguese
Portuguese Ukrainian
Ukrainian Arabic
Arabic Italian
Italian Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian Greek
Greek Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Macedonian
Macedonian Malay
Malay Maltese
Maltese Norwegian
Norwegian Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Romanian
Romanian Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Urdu
Urdu Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Yiddish
Yiddish